Get ready for an exciting journey into the world of phlebotomy with our Order of Draw Phlebotomy Quiz! This interactive experience will guide you through the crucial steps of blood collection, ensuring you have the knowledge and skills to become a top-notch phlebotomist.
As you progress through the quiz, you’ll uncover the rationale behind the established draw order, explore the different types of blood collection tubes, and learn how to handle exceptions and special cases with confidence.
Draw Order Overview
In phlebotomy, draw order refers to the sequence in which blood samples are collected from different tubes containing various additives or anticoagulants. This order is crucial to ensure accurate and reliable laboratory results.
The correct draw order is established based on the specific tests ordered and the additives or anticoagulants present in the tubes. These additives play a vital role in preventing blood clotting, preserving the integrity of the sample, and stabilizing certain analytes.
Rationale and Importance
- Preventing Contamination:Following the correct draw order helps prevent contamination of samples with additives or anticoagulants from previous tubes.
- Preserving Sample Integrity:Additives and anticoagulants are designed to preserve specific analytes in the blood sample. Drawing in the correct order ensures that the proper additives are used for each test, preventing interference or degradation of the sample.
- Ensuring Accurate Results:By adhering to the draw order, laboratories can ensure that the samples are processed and analyzed correctly, leading to accurate and reliable test results.
Blood Tube Types
In phlebotomy, various types of blood collection tubes are used, each designed for specific purposes. These tubes are color-coded for easy identification, ensuring accurate sample collection and analysis.
The order of draw phlebotomy quiz can be a tricky one to master, but it’s an important skill for any medical professional. Just like the color by number Newton’s laws activity, understanding the order of draw is crucial for accurate blood collection.
The first tube drawn should be the one with the highest priority test, and the last tube should be the one with the lowest priority test. By following the correct order, you can ensure that the blood samples are collected in the correct order and that the tests are performed accurately.
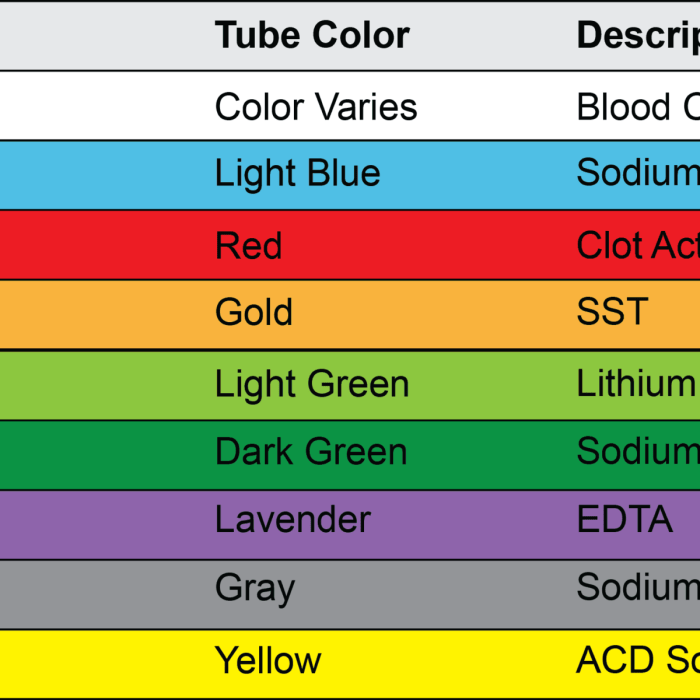
Color-Coding System
The color-coding system for blood tubes is standardized to facilitate quick and accurate sample handling. Each color represents a specific type of additive or anticoagulant present in the tube, which helps preserve the integrity of the blood sample.
Tube Types and Additives
The following table summarizes the commonly used blood tube types, their additives, and their intended purposes:
| Tube Color | Additive | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Red | No additive | Serum chemistry, serology |
| Gold (with gel separator) | Clot activator, gel separator | Serum chemistry, serology |
| Blue (light blue) | Sodium citrate | Coagulation studies |
| Green (dark green) | Lithium heparin | Plasma chemistry, blood banking |
| Lavender (with EDTA) | Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) | Complete blood count (CBC) |
| Gray | Sodium fluoride, potassium oxalate | Glucose determination |
Draw Order Sequence
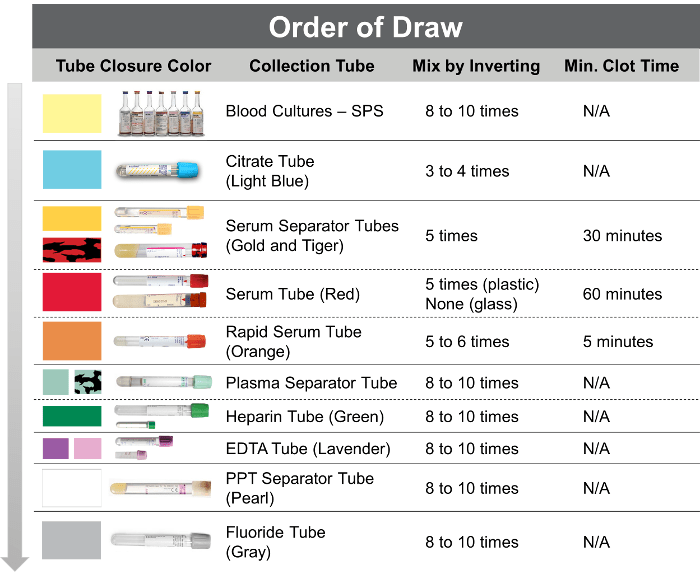
Establishing a standard draw order sequence is crucial for routine blood collection, ensuring patient safety and minimizing contamination risks. This sequence guides phlebotomists in drawing blood in a specific order, prioritizing tubes with additives that can affect subsequent test results.
Step-by-Step Guide, Order of draw phlebotomy quiz
- Blood Culture Tubes:These are drawn first, before any other tubes, to prevent contamination from skin flora or other sources.
- Coagulation Tubes (Light Blue):These contain sodium citrate, which prevents blood from clotting. They are used for coagulation tests.
- Serum Separator Tubes (Red, Yellow, or Gold):These contain a gel or clot activator that separates serum from the clot. They are used for a wide range of tests, including chemistry, serology, and immunology.
- Heparin Tubes (Green):These contain heparin, an anticoagulant that prevents blood from clotting. They are used for hematology tests, such as complete blood count (CBC).
- EDTA Tubes (Lavender):These contain ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), an anticoagulant that prevents blood from clotting. They are used for hematology tests, such as CBC and differential.
- Glycolytic Inhibitor Tubes (Gray):These contain sodium fluoride and potassium oxalate, which inhibit glycolysis and preserve glucose levels. They are used for glucose testing.
It’s important to adhere to this draw order sequence to avoid contamination and ensure accurate test results. Proper training and adherence to protocols are essential for phlebotomists to maintain patient safety and provide reliable laboratory data.
Exceptions and Special Cases
While the standard draw order is generally followed, there are certain exceptions and special cases where the order may need to be modified to ensure accurate and reliable test results.
Factors that may necessitate a deviation from the standard draw order include the following:
Blood Cultures
Blood cultures are used to detect bacteria or fungi in the blood. For blood culture collection, a specific blood culture bottle is used, which contains a growth medium that supports the growth of microorganisms. It is crucial to draw the blood culture bottle first to avoid contamination of the sample with skin flora or other microorganisms present on the skin’s surface.
Tests Requiring Specific Tube Additives
Certain tests require the use of blood collection tubes containing specific additives to ensure the stability and integrity of the sample. For instance, tubes containing anticoagulants, such as EDTA or heparin, are used for tests that require the prevention of blood clotting.
Tubes containing clot activators are used for tests that require serum, which is the liquid component of blood that separates after clotting.
Documentation and Verification: Order Of Draw Phlebotomy Quiz
Proper documentation is crucial in phlebotomy to ensure patient safety and accurate test results. Phlebotomists are responsible for accurately recording patient information, including name, date of birth, medical record number, and the tests ordered.Phlebotomists must also verify that the blood tubes are labeled correctly with the patient’s information and the time and date of collection.
This helps to prevent errors in sample identification and ensures that the correct tests are performed on the patient’s blood.
Consequences of Incorrect Documentation and Labeling
Incorrect documentation and labeling can have serious consequences. If patient information is not recorded correctly, the test results may be inaccurate or the patient may not receive the correct treatment. If blood tubes are not labeled correctly, the samples may be mixed up or lost, which can delay or even prevent the patient from receiving the necessary medical care.
Patient Education
Patient education is crucial for a successful draw order process. Informed patients can assist phlebotomists and ensure the accuracy and efficiency of blood draws.
Phlebotomists should clearly explain the draw order process to patients, including the sequence of tubes, the importance of proper identification, and the potential consequences of not following the draw order. This can be done through verbal communication, written instructions, or a combination of both.
Benefits of Patient Understanding and Cooperation
- Reduced risk of incorrect sample collection
- Improved accuracy and reliability of test results
- Increased patient satisfaction and trust
- Smoother and less stressful experience for both the patient and the phlebotomist
FAQs
What is the significance of following the correct order of draw?
Adhering to the order of draw prevents contamination of blood samples and ensures accurate test results.
How do I remember the order of draw?
Use the mnemonic “Red, Yellow, Green, Blue, Lavender” to recall the sequence of blood tube colors.
What are some exceptions to the standard order of draw?
Exceptions may occur when specific tests require specialized additives or when blood cultures are needed.