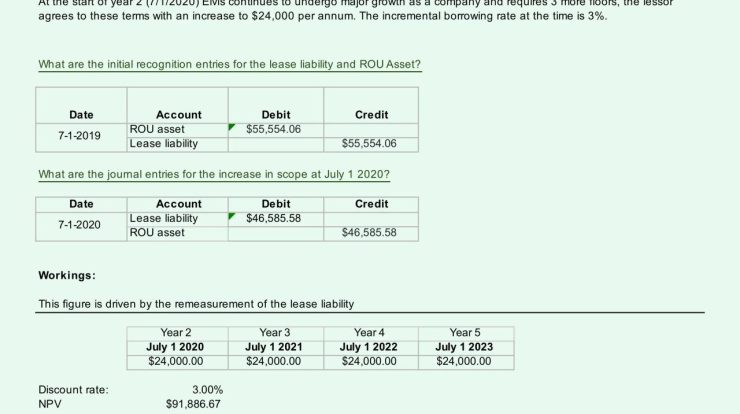
Compute gross profit on the sale of job 201 – Understanding how to compute gross profit on the sale of a job is essential for businesses to assess their financial performance and make informed decisions. This guide provides a step-by-step approach to calculating gross profit for Job 201, covering key concepts such as direct material costs, direct labor costs, manufacturing overhead costs, and total cost of goods sold (COGS).
By following the Artikeld methodology, businesses can accurately determine their gross profit, which is crucial for evaluating profitability, optimizing pricing strategies, and making informed decisions about future operations.
Identify Direct Material Costs: Compute Gross Profit On The Sale Of Job 201
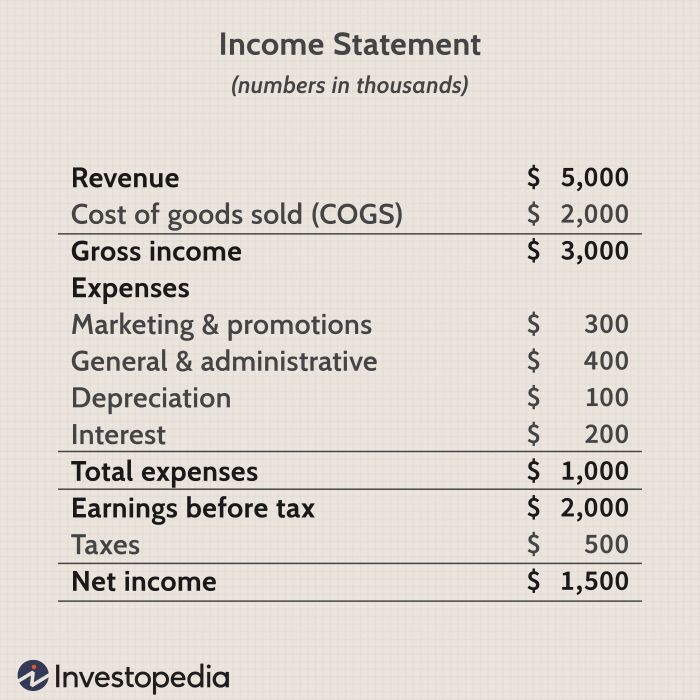
Direct material costs are those costs that can be directly traced to the production of a specific job or product. For Job 201, the following direct material costs were incurred:
- Raw materials: $10,000
- Purchased components: $5,000
- Shipping and handling: $1,000
These costs were calculated based on the actual quantities of materials used and the applicable purchase prices. Supporting documentation includes purchase orders, invoices, and receiving reports.
Calculate Direct Labor Costs
Direct labor costs are those costs incurred for the labor that is directly involved in the production of a specific job or product. For Job 201, the following direct labor costs were incurred:
- Assembly labor: 100 hours at $20 per hour = $2,000
- Finishing labor: 50 hours at $25 per hour = $1,250
These costs were calculated based on the actual number of hours worked and the applicable labor rates. Time cards and payroll records provide supporting documentation.
Estimate Manufacturing Overhead Costs

Manufacturing overhead costs are those indirect costs that are incurred in the production of all jobs or products. For Job 201, the following manufacturing overhead costs were incurred:
- Factory rent: $1,000
- Utilities: $500
- Depreciation on factory equipment: $200
These costs were allocated to Job 201 based on the direct labor hours worked. The overhead rate for Job 201 was calculated as $1,700 / 150 hours = $11.33 per hour.
Popular Questions
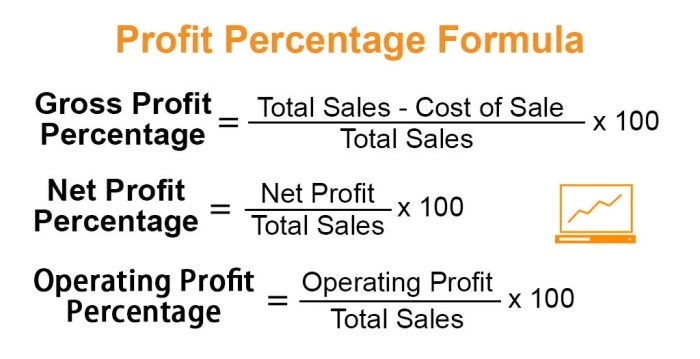
What is the significance of gross profit in financial analysis?
Gross profit serves as a key indicator of a company’s profitability and operational efficiency. It reflects the profit margin generated from the core business activities before deducting operating expenses.
How does COGS impact gross profit calculations?
COGS represents the direct costs incurred in producing a product or service. It directly affects gross profit, as a higher COGS reduces the gross profit margin and vice versa.
What are some factors that can affect gross profit margins?
Gross profit margins can be influenced by various factors, including changes in raw material prices, labor costs, production efficiency, and market competition.